We introduced before
Application cases of 12kW laser-arc hybrid welding for ship plates above 14mm:
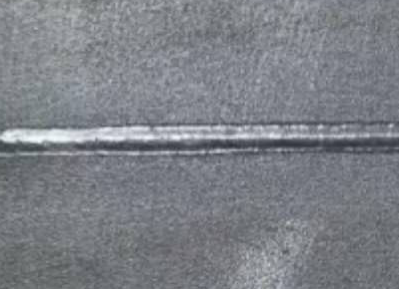
In this issue, we will separately talk about 10,000-watt single laser deep penetration welding.
With the continuous development of commercial high-power lasers, the use of high-power laser welding technology for machinery, automobile body and parts manufacturing, metallurgical industry, electronics, chemical industry, medical equipment, aerospace and packaging and other fields is bound to be the mainstream trend of laser processing technology in the future.
Laser deep penetration welding is a kind of self-fusion welding. In laser self-fusion welding, the primary metal is melted. There is no need to add weak solder or flux. This also means a cleaner weld and no need to worry about the introduction of new elements. The sewing performance has changed, which also reduces the cost of adding other equipment.
In high-power laser deep penetration welding, a deep and narrow welding hole is always produced, and the higher the laser power, the deeper the hole. When the metal vapor recoil pressure generated by the laser beam in the small hole is balanced with the surface tension and gravity of the liquid metal, the small hole does not continue to deepen and forms a stable small hole.
After the laser deep penetration welding small hole is formed, due to the sidewall focusing effect, the depth of the small hole increases until the laser energy attenuates to a certain value, the depth of the small hole no longer increases, and finally a deep and narrow weld is obtained.
However, because there is no filler metal during welding, there are very high requirements for the gap of the welded joint. The butt gap of the workpiece is required to be small and large misalignment is avoided. Therefore, the single-pass laser butt welding of thick plates generally uses pure laser welding to avoid excessive surface collapse of the weld.
Compared with traditional welding methods, high-power laser deep penetration welding has the following advantages
● The laser radiation has large illuminance, small heating range, small heat input, so welding deformation and welding residual stress are small, and the welding precision is high;
● Fast heating and cooling speed, narrow heat affected zone and good mechanical properties of the joint;
● It can weld high melting point materials that are difficult to weld by general methods, such as Zr, W, Mo, cemented carbide, ceramics, etc.;
● Large aspect ratio, fast welding speed and high production efficiency;
● It can be welded in long-distance or inaccessible parts.
However, for laser welding with high energy input and high-power density, various welding defects are easily generated during the welding process, and the causes of thick plate defects are much more complicated than thin plate welding.
During the welding process of high-power fiber laser thick plates, the small holes are extremely unstable, and welding defects such as spatter, surface collapse and bottom hump are easy to occur. This not only affects the beauty of the weld, but also affects the mechanical properties of the weld, which largely limits the application of high-power lasers in thick plate welding.
Splash

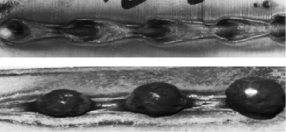
Surface collapse and bottom hump
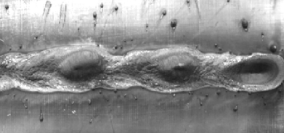
Surface hump
In order to avoid welding defects
Generally can be improved from the following aspects
1 Welding speed
The welding speed will directly affect the magnitude of the heat input density, thereby affecting the penetration of thick plate welding.
2 Defocus
Changing the defocus amount will affect the spot size on the surface of the test piece, and affect the energy density reaching the surface of the test piece and the small hole, and affect the ability of the laser to penetrate the workpiece. And to a large extent will affect the spatter and weld morphology.
3 shielding gas
The shielding gas is divided into front shielding gas and back shielding gas. The front shielding gas can blow away the plasma generated in the 10,000-watt laser welding process, and can effectively protect the front welding seam forming and prevent metal oxidation.
4 Butt gaps
Properly increasing the butt gap is conducive to the flow of the molten pool and can eliminate the surface protrusion caused by the enlarged weld structure. However, when the gap is large, the laser energy is prone to loss, and the molten metal cannot fill the gap between the welds and cause the weld to collapse.
We use Raycus 10,000-watt laser (RFL-C12000) to conduct welding experiments on 12mm thick plates of different materials, let's take a look at the welding effect!
12mm stainless steel plate splicing welding
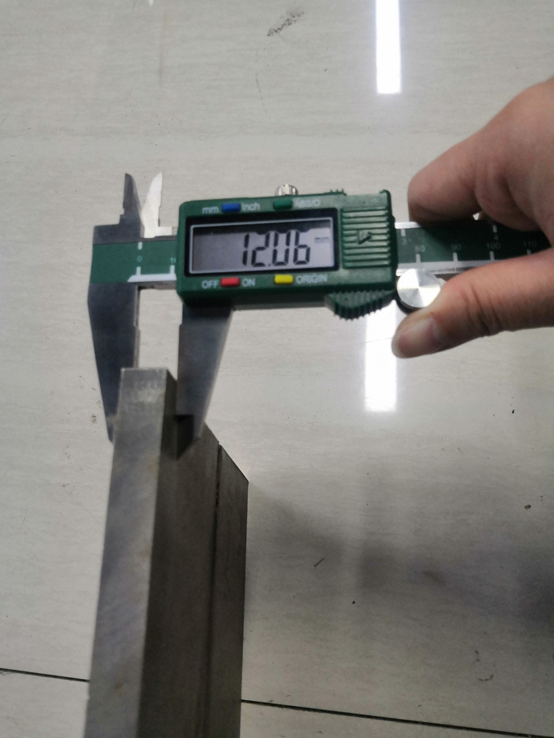

model power(W) speed(m/min)
RFL-C12000 10500 1.2

Weld cross section

Front side of weld

The back of the weld
12mm X86 pipeline steel splicing welding
model power(W) speed(m/min)
RFL-C12000 10000 1
Front side of weld
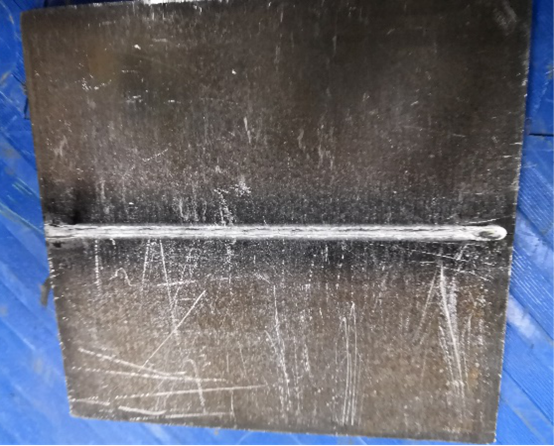
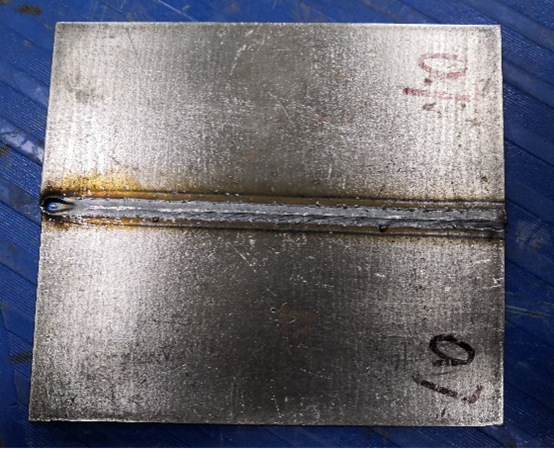

Back side of weld
12mm carbon steel plate fillet welding
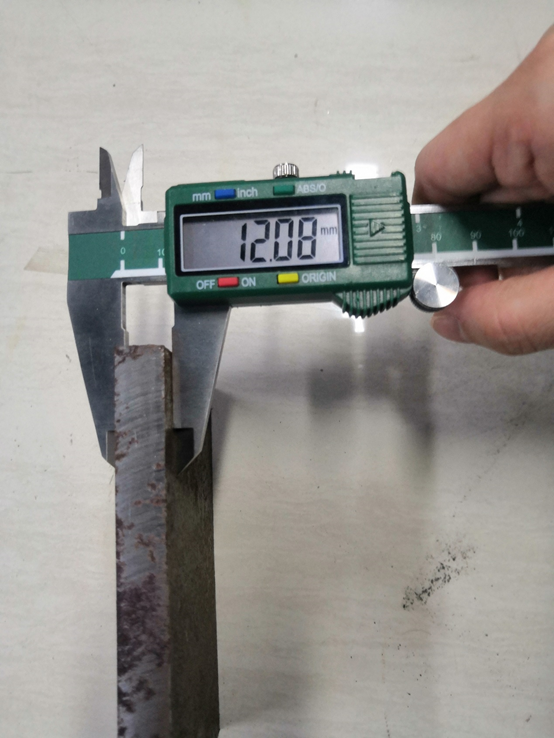

model power(W) speed(m/min)
RFL-C12000 10000 1
Front side of weld
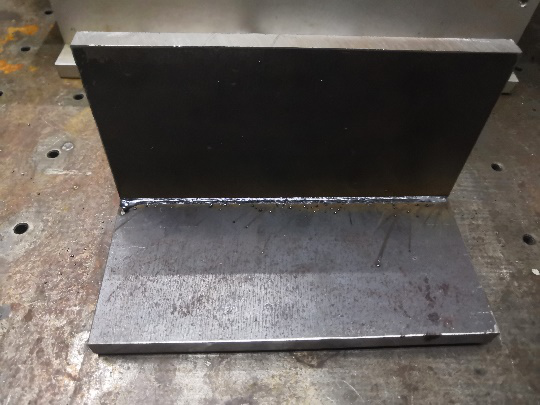


Back side of weld
The front and back sides of the welds of the three materials are formed relatively uniformly, the welds are narrow and the width of the welds on the upper and lower surfaces is basically the same, and the upper and lower surfaces of the welds have no surface collapse and bottom hump. Except carbon steel has a small amount of spatter, stainless steel and pipeline steel also have no spatter, and the weld cross-section is in the shape of "I", which achieves a good welding effect.
12mm carbon steel or stainless-steel arc welding and laser welding comparison
Laser welding VS arc welding
Welding speed (m/min)
1.2 VS max 0.4
Number of welding passes
Single channel VS 3-4 channel
Groove
No bevel VS need to open a large bevel


